 Exercise: React Router part 1 (Basic)
Exercise: React Router part 1 (Basic) Exercise: React Router part 1 (Basic)
Exercise: React Router part 1 (Basic)Idea: Introduction to React-Router (BrowserRouter, Route, and Link).
Background: https://blog.pshrmn.com/entry/simple-react-router-v4-tutorial/ and https://reacttraining.com/react-router/web/guides/quick-start
In this exercise you have to create a very basic React App with routing.
Step 1 (create the initial React-App and install the react-router-dom lib)
Create a new React App: 'basic' by running 'npx create-react-app basic'
Navigate to your new project directory and install the react-router-dom library locally by running 'npm install --save react-router-dom@5.2.0'.
Verify that your initial project is up and running with: 'npm start'.
Step 2 (Clean the default src-folder)
Delete all files in the src-folder
Step 3 (App.js)
Create a new App.js fil in the src-folder.
Import React from 'react', create a simple App-component and make a default export of the component:
Step 4 (index.js)
Create a new index.js fil in the src-folder .
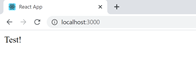
And verify that it still works:
Step 5 (Home.js)
Create a new 'landing page' to the app (Home.js in the src-folder). Add a simple component like:
Step 6 (Page2.js)
Create a second ' page' to the app (Page2.js in the src-folder). Add a simple component like:
Step 7 (Update the index.js file)
Import the BrowserRouter component from 'react-router-dom' and wrap it arround the App-component (routing will now be awailable all over in our App).
Step 8 (Update the App.js file)
Import the Route Component from 'react-router-dom' and the two components 'Home' and 'Page2'. Insert 2 Routs: path='/' for the Home-component and path='/page2' for the Page2-component:
Notice: The 'exact' keyword. If we omit 'exact' - the 'Home' component will be rendered on both 'pages' (since '/page2' contains '/')
Verify that your Routing is working:
a) Try both: 'localhost.3000' and 'localhost:3000/page2'.
b) What happens if you type: 'localhost:3000/page3' ?
c) Is the Browser history working (<- and ->) ?
d) Test also the 'exact' keywork - try without the keyword!
In Single Page Applications (SPA) we don't use <a href='....> since it causes a brand new page (and clears the state of the App). In React Apps we are using the Link component from 'react-router-dom', it prevents the reload and the loss of the apps state.
Step 9 (Update the App.js file)
Import the Link Component from 'react-router-dom' and add 2 Link-components with links to the 'Home' and 'Page2'
Verify that your link is working (notice the url in the Browser)
Route parameter or URL parameter are a wellknown technique for passing values to a page during page-navigation, e.g '/user/1' if we wanted to view information about user #1.
In this exercise will we use Route Params to send a value to a nested page.
Step 10 (Update Page2.js)
Add imports of {Route} from 'react-router-dom', Page3 and Page4 (to be created in step 11-12). Add the following Route-components for routing to Page3 and Page4.
Notice: Page3 and Page4 are nested (sub) pages to Page2 and '/:id' specify the Route parameter
Step 11 (Page3.js)
Create a new file: Page3.js:
Step 12 (Page4.js)
Create a new file: Page4.js:
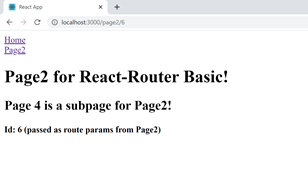
Note: The library passes a Props called match to the component, to access the Route Params 'id' we use: 'match.params.id'.
Verify - that you get something like this:
Now is time for a little refactoring. We will use the functions useParams() and useRoutMatch() from the libary 'react-router-dom' and the component Switch and Link, also from 'react-router-dom'.
Step 13 (Refactor Page4.js)
Add an import for { useParams } from 'react-router-dom' and refactor Page4 to fetch the id parameter by using the function useParams():
Step 14 (Refactor Page2.js)
Add an import for Switch, Link and useRouteMatch from the 'react-router-dom' library. Refactor Page2 to get the path and url using the function useRouteMatch().
Refactor the Route-components to use path
Wrap a Switch-component around all the Route-components (Switch renders the first child of <Route> or <Redirect> that matches the location).
Add a Link-component to Page4, using url:
Verify - that you get something like this:

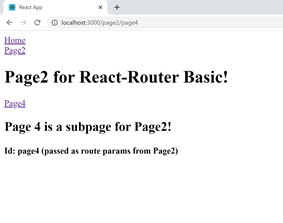
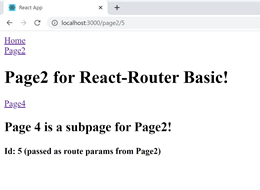
Notice urls and the values passed as params
Congratulation! - Yes Route is nice and simple!
/ Henrik H